Torch
torch包含了多维的数据结构以及基于其上的数学运算。它提供了多种实用工具,具有CUDA对应的实现
张量 Tensors
|
|
|
|
判断是否为张量,如果是pytorch张量,则返回True
我们提出对神经网络语言模型进行的一个扩展,以使其预测适应最近的历史。我们的模型是内存增强网络的简化版本。它将过去隐藏的激活存储为内存,并通过当前隐藏激活的点积访问它们。这种机制非常有效,可以扩展到非常大的内存大小。我们还在神经网络中使用外部存储器和基于计数的语言模型使用缓存模型之间建立了联系。我们在几个语言模型数据集上进行演示,我们的方法比最近的内存扩展网络性能更好。
语言模型是单词序列的概率分布,具有许多应用,如machine translation,speech recognition 或dialogue agents。虽然传统的神经网络语言模型已经在这个领域获得了最先进的性能,但是它们缺乏适应其最近历史的能力,这限制了它们在动态环境中的应用。最近的解决这个问题的方法是用external memory来扩充这些网络。这些模型可能会使用外部存储器来存储新的信息并适应不断变化的环境。
虽然这些网络在语言建模数据集上取得了很好的结果,但它们在计算上相当昂贵。通常,他们必须学习一个可以参数化的机制来读取或写入存储单元。这可能会限制其可用内存的大小以及可以训练的数据量。在这项工作中,我们提出了一个非常轻量级的选择,它可以共享内存扩展网络的一些特性,特别是随着时间的推移动态调整的能力。通过最小化内存的计算负担,我们可以使用更大的内存并扩展到更大的数据集。我们在实践中观察到,这使我们能够在不同的语言建模任务上超越记忆增强网络的性能。
今天介绍一个python库--wordcloud,这个库的主要功能是对一个文本中的单词进行统计,并且以词云的方式进行展示,从生成的图片中,我们可以直观的发现哪些单词出现的频率较高,一个很有意思的用途就是统计一个会议中,提交论文的主题是哪些,从而看出当前研究的趋势。
|
|
|
|
在处理文字时,处理庞大但是稀少的语言是很困难的。即使对于一个晓得语料库,神经网络也需要支持数以千计的离散输入和输出。
除了原始数字外,将单词表示为one-hot向量的方法无法捕获任何有关单词之间关系的信息。
Word Vector 通过在多维向量空间中表示单词来解决这个问题。这样就可以将问题的维度数十万减少到数百。而且向量空间能够从距离向量之间的夹角来捕获单词之间的语义关系。
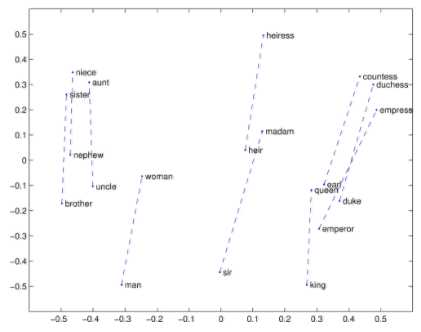
现已有一些创建Word Vector的技巧。word2vec算法可预测上下文中的单词(例如”the cat”最可能出现的单词是”the mouse”),而Glove向量则基于整个语料库的全局计数。glove最大的特点就是可以轻松的下载多套预先训练好的词向量。
In contrast to previous models which predict next word based on one previous word and hidden state, our language CNN is fed with all the previous words and can model the long-range dependencies in history words, which are critical for image captioning.
Image captioning model should be capable of capturing implicit semantic information of an im-age and generating humanlike sentences. Most image captioning models follow the encoder-decoder pipeline.
Although models like LSTM networks have memory cells which aim to memorize history information for long-term, they are still limited to several time steps because long-term information is gradually diluted at every time step
To better model the hierarchical structure and long-term dependencies in word sequences we adopt a language CNN which applies temporal convolution to extract features from sequences.
To summarize, our primary contribution lies in incorporating a language CNN, which is capable of capturing long-range dependencies in sequences, with RNNs for image captioning.
We extend current models to deal with two key challenges present in this task: corpora and vocabulary sizes, and complex, long term structure of language. We perform an exhaustive study on techniques such as character Convolutional Neural Networks or Long-Short Term Memory, on the One Billion Word Benchmark.
Models which can accurately place distributions over sentences not only encode complexities of language such as grammatical structure, but also distill a fair amount of information about the knowledge that a corpora may contain.(提取大量关于语料库可能包含的知识的信息).
Language Modeling can apply in speech recoginition, machine translation, text summarization etc. (such as word error rate for speech recognition, or BLEU score for translation).
When trained on vast amounts of data, language models compactly extract knowledge encoded in the training data. For example, when trained on movie subtitles, language models are able to generate basic answers to questions about object colors, facts about people, etc.
|
|
out[]
[([‘me’, ‘gusta’, ‘comer’, ‘en’, ‘la’, ‘cafeteria’], ‘SPANISH’),
([‘Give’, ‘it’, ‘to’, ‘me’], ‘ENGLISH’),
([‘No’, ‘creo’, ‘que’, ‘sea’, ‘una’, ‘buena’, ‘idea’], ‘SPANISH’),
([‘No’, ‘it’, ‘is’, ‘not’, ‘a’, ‘good’, ‘idea’, ‘to’, ‘get’, ‘lost’, ‘at’, ‘sea’], ‘ENGLISH’)]
深度学习的浪潮袭来,现已在各个领域中应用。深度学习的表现令人叹为观止,不得不说我们迎来了依靠深度学习的人工智能学习时代。
人工智能,让世界更美好。
这一章主要是通过学习 Stanford cs224d 课程已经阅读一些有些的博客所作出的总结。
简言之,一个线性表是n个数据元素的有限序列。
在复杂的线性表中,一个数据元素可由若干个数据项(item)组成。在这种情况下,常把数据元素称为记录(record),含有大量记录的线性表又称为文件(file)。
|
|